独学プログラマーの私がプログラミング初心者に贈るたったひとつの教訓

Quincy Larson
Free Code Campの講師です。Free Code Campではコーディングの学習を、非営利活動を通じて支援しています。
この記事はFreeCodeCampからの翻訳転載です。配信元または著者の許可を得て配信しています。
A Cautionary Tale of Learning to Code. My own.昔の私は、スーツを着てオフィスで働く傍ら、漠然としたスタートアップのアイデアを温めているような男でした。ですがある日、コーディングについて学ぶことにしたのです。
プログラミングとの出会い
ある人が終業後に自慢げに話しているのを立ち聞きしたところによると、その人はRubyと呼ばれるプログラム言語を使って、自分の一連の業務を簡単に自動化したというのです。私は「ふぅん、Rubyね」と思って帰宅し、Googleで検索して15秒も経たないうちに、適当なRubyの初心者チュートリアルに取り組んでいました。
その一週間後、私はプログラマーの集まりに初めて顔を出しました。皆がScala、Clojure、Goといった言語について話し込んでおり、吸収すべき知識にあふれていました。私はオライリーの本を三冊借り、それぞれ約50ページずつくらいまで進めました。

そんなある日、友人からEmacsを習得するよう勧められ、使っている設定ファイルをを譲り受けました。自分の好みでこの設定ファイルを書き換えられるよう、私は数時間かけてLisp構文を学習しました。
その後、Emacsを使っている私のところにある人がやってきて、こうたずねました。「なぜEmacsを使っているの? Vimの方がいいのに」「ふむ、Vimね」そうして、今度はVimの大量のキーボードショートカットを覚えることにしました。
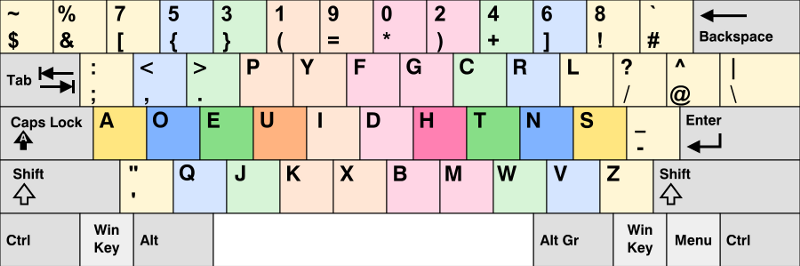
この時、より素早く入力ができればより速くコードが書けると思い、キーボードをプログラマー御用達のDvorak配列のものに切り替えました。客観的に見ても、プログラマーにとって一番効率のいいキーボードだと思っています。
ノートパソコンでLinuxの起動に成功したり、1分あたり10単語のペースで入力ができるようになったりしながら、私は教本とUdacityのオンライン講座を通してPythonを学びました。
念願のエンジニア就職
7か月に及ぶ、苦難の独学とコーディングの勉強会などの参加を経て、私は初のSEの仕事にこぎつけました。
技術主任との面接の間は、私は学んだツール、使用している複雑な設定について話し、技術主任は丁寧に相槌を打ちながら話に耳を傾けていました。そして私が自分の知識をひけらかし終えると、私は身の程を思い知るような鋭い見解を、彼に告げられます。
「ほとんどの場合、物事を実現するための方法は様々ですが、実際に有効なのはその内一握りなのですよ」そう言って、彼は使い古しのMacBookをよこし、開発部門に私を放り込みました。
この4年前、この企業はRuby on Railsを使って製品を作ることを決定していました。この決定にはとても熱心に取り組んでおり、当時のコードはその時点でもまだ製品に使われていました。製品に使われるUbuntu Linuxサーバに似た環境のため、技術者は皆使用していたのはMacBookでした。
VimかEmacsかで揉める代わりに、全員が統合開発環境(IDE)のRubyMineをほぼ初期設定で使ってしていました。これは、技術者は開発環境の差異を気にせずに、同僚の隣に移動してすぐに、ペアプログラミングを開始できるように意識してのことです。これにより、複数の技術者が協力体制を敷くにあたって発生する面倒事や無意識の抵抗感の大半を取り除くことに成功していたのです。
この会社で働くにあたって、私がRuby on Railsを知らないことは会社的に問題とはなりませんでした。それまでPythonやDjangoの習得に注力し、ハッカソンで入賞したことで、いずれRailsを習得できるだろうと判断されたのでしょう。
個人と企業のプログラミングの違い
最初の数週間はきついものでしたが、これは新しいチームや未知の言語、フレームワーク、ソフトウェアに翻弄されたからではありません。そこで触れるもの全てにおいて、私の今までの勉強方法がいかに非効率でマゾヒスティックなやり方であったと突きつけられたからです。
意味も分からずコマンドラインでツールをインストールしたり、Linuxのドライバーのバグと戦ったり、コード中の閉じかっこの書き忘れで頭を抱えたりということを、私は図書館や喫茶店で数か月にわたって一人で続けていました。
また、考え付く限りのオンライン講座の受講も開始しました。はじめてネットに作ったものを乗っけることができたのは、それを5ヶ月ほど続けた頃だったかと思います。
この経験は、プログラミングは苦しく無益な作業であるという印象を私に与えました。多くのプログラマーが社交的ではないのは、きっとコーディングを学ぶことにトラウマを持ち、それを抑え込んでいるからだと思いました。

そんなイメージも入社して変わりました。同僚は、IDEの自動検出のおかげで構文エラーに滅多に出くわさず、あの頃の私とは対照的です。同僚のMacBookは「ちゃんと」機能しているのです。
彼らはエラーメッセージに出くわし、検索などの情報を調べて数分しても解決できないとき、他の同僚にすぐメッセージを送って協力してもらいます。あるいは同僚の机に気軽に立ち寄って、ペアプログラミングを開始したりもできるのです。
自意識や、エリート意識などというものとは無縁です。プログラミングが単調作業だという感覚もありません。あるのはフレンドリーで大人な人たちとの建設的な会話の連続で、私のように孤独にコーディングを学ぶ人は一部でした。
選択と集中で技術力を高める
私のいる部署はツールの開発に取り組んでいました。ここではPassion ProjectやハッカソンでAngular.jsのような新しいJavaScriptのフレームワークの経験を積むのを除けば、現在使われている技術を習熟することに注力します。彼らはコード資産に新たに何かを追加するなどといったことに関しては、保守的でした。
同様の特徴はThoughtBotのような場所でも見られ、そこでは少数の有効なツール群(この場合、Rails、Vim、PostgreとRedis)にこだわっています。少数の重要なツールに集中することで、技術者は熟練し、容易に相互連携ができるようになるのです。
ここで目の前の現実に立ち戻りましょう。高い生産性を持つソフトウェア技術者集団が少数のツールに集中することで力を発揮するとして、プログラミングを学ぶ人間も、同様に使うツールを絞り込むべきなのでしょうか? オンラインのコーディング講座や特訓会では、そう考えられているようです。
しかし個人的には、選択肢がありすぎて、何を学ぶべきか選ぶのはとても困難です。私自身、同じ場所を行ったり来たりして、目標を次々変えていた経験からよく分かります。優秀なプログラマーのスキルセットはT型として説明されますが、広い分野の知識を浅く持つ一方で、少なくとも一つの分野について深い知識を持つというものです。私の場合は、数か月にわたるストレスと激務の結果、むしろ横棒型になってしまいました。
私と同じ方法でコーディングの学習を行った人をたくさん見てきたので、おそらく同様の人は無数にいることでしょう。これらの人は皆、途中で挫折し、プログラマーになる夢を諦めてきました。読者であるあなたは違う結果になることを願います。
学習する領域は絞り込むべきという教訓
ここで、私の考えるコーディング初心者が犯しがちな間違いを次に挙げます。
- 使用する言語やフレームワークを頻繁に変え、それらすべてに習熟できると思い込む
- 一般的で、相互の連携に信頼がおけるツールではなく、馴染みのないツール群で開発環境を固める
- 基礎となる技術を習得する前に、目新しく面白いという理由でDockerやFamo.usといったツールを学ぼうとする
自身を反面教師として一言助言するとすれば、「絞り込むこと」に尽きます。
領域の絞り込みを念頭にコーディングの学習計画を立てましょう。もう既に自分で絞り込まれていると考えるなら、すぐにこの記事を読むのをやめて、自分の学習に戻ってください。あなたがせっかくフォーカスできているのに、この記事によって気を逸らしたら嫌ですからね。
コーディングの学習計画がまだ絞り込まれていない方がいるのであれば、朗報です。今すぐに絞り込むことができます。数分で終わりますが、少し困難な選択になってしまうかもしれません。あなたのするべき選択は次の通りです。
学習領域を絞り込む方法
1. 自分のキャリアの根幹としたいソフトウェア開発の分野を一つ選びましょう。Web、モバイル、ゲーム、または組み込み機器などです。融通の利きやすいWebなどはおすすめです。求人も教材リソースもネットにあふれています。ウェブ以外のものに熱意を持っているなら、今すぐこのブログから出て、グーグル検索なりで勉強を始めましょう!
2. JavaScript、RubyまたはPythonの内、学習する言語を一つ選びましょう。それぞれに強みがありますし、Node.js、Rails、Djangoなどのツールを利用すれば、Webアプリも作ることができます。特に好みがなければ、最もポピュラーなJavaScriptをお勧めします。
3. オンラインのコーディング講座を一つ選びましょう。分かりやすいものとしては、JavaScriptでのFree Code Camp、RubyのThe Odin Projectです。自分の選んだ講座を設計した講師を信用し、一つ一つ用意された順番に取り組んでいきましょう。
まとめ
一度これらの選択をしたら、進むべき道は単純です。周辺で目を引くツール群に惑わされずに気を確かに持ちましょう。一度に30分ずつで構いませんから、自分の選んだ講座に週7日取り組んで、勢いを保ちましょう。今日行った自分の決断を信じて、自信を保ってください。
そして、お忘れなく。忍耐があれば誰でも、優れたプログラマーになれるのです。あなたも例外ではありません。